The human body is a miraculous machine that can do amazing things, like ovulate late. For many people, ovulation occurs around day fourteen of their cycle. However, for some people, ovulation can occur later in the cycle. This can be due to a number of factors, including stress, illness, and diet. Late irregular ovulation can cause difficulty in getting pregnant because it reduces the time frame during which pregnancy can occur. In this blog post, let’s get to know more about what is late ovulation and what we can do about it.
Contents
What is late ovulation?
Late ovulation is a condition in which ovulation does not occur until after day 21 of the irregular cycles. Late ovulation can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, illness, and hormonal imbalance. Women who experience late ovulation may have difficulty conceiving, as sperm may no longer be viable after 3-5 days. Treatment for late ovulation depends on the underlying cause and may include lifestyle changes, medication, or fertility treatments.
If the egg hasn’t been fertilized by sperm, ovulation will be followed by a luteal phase in which hormones are released to trigger the shedding of the uterine lining.
What are the symptoms of late ovulation?

Most women know when they ovulate because they feel the symptoms. The most common symptom of ovulation is a change in the cervical mucus. It becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy. This is called fertile mucus and it means that you are most likely to get pregnant if you have sex during this time. Other symptoms of ovulation include cramps, bloating, a feeling of fullness in the pelvis, and breast tenderness. If you don’t usually notice these changes, you may want to start tracking your menstrual cycle so that you will know when to expect ovulation.
What causes late ovulation?

There are many potential causes of late ovulation, including:
- Hormonal imbalance – A lack of progesterone or an over-abundance of estrogen (reproductive hormones) can delay ovulation.
- Poor egg quality – If the eggs are old or not healthy, they may not be released by the ovaries.
- PCOS – Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a condition that affects the way the ovaries work and can lead to delayed ovulation.
- Stress – When you’re feeling stressed, your body produces higher levels of cortisol which can interfere with the normal hormone production needed for ovulation.
- Weight issues – Being overweight or underweight can impact your hormone levels and disrupt your menstrual cycle.
Stress
Stress can delay ovulation.

In a study of women who were trying to get pregnant, those who reported higher levels of stress had a harder time ovulating. The women in the study were asked to report their stress levels in daily diaries, and researchers found that those with the highest stress levels were more likely to have delayed ovulation.
“We know that stress can affect how a woman’s body functions,” said study author Anne Marie Jukic. “This is the first study to look at how stress may delay ovulation.
Medications
Most medications will not interfere with ovulation. However, there are a few that may inhibit ovulation. Some anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), can delay ovulation. Birth control pills can also delay ovulation, as can some antipsychotic medications. If you are taking any of these medications and are trying to conceive, talk to your doctor about possible alternatives. Hormone therapy. Human gonadotropins contain follicle-stimulating hormones and sometimes luteinizing hormone.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects 1 in 10 women of childbearing age. PCOS is the most common cause of female infertility. It can also lead to long-term health problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
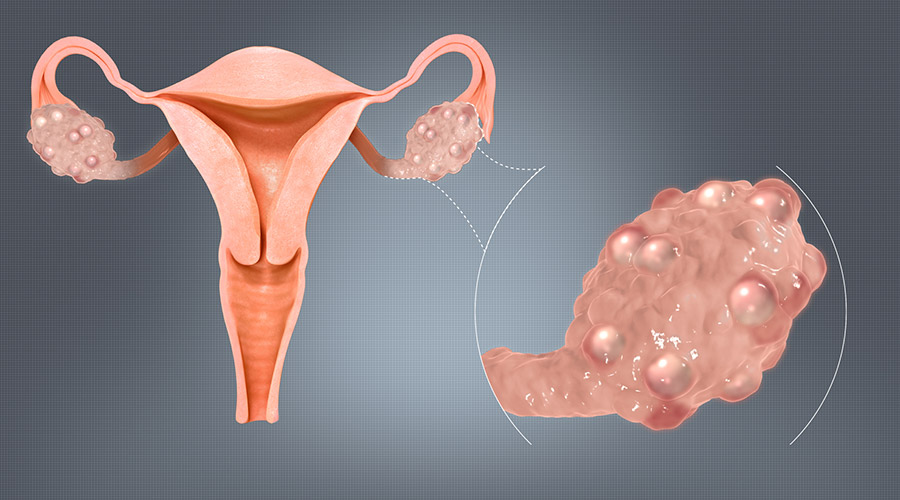
PCOS is a problem with how your body makes hormones. The ovaries make too many male hormones (androgens). This can prevent ovulation, the release of an egg each month. PCOS also causes small cysts to form on the ovaries.
The signs and symptoms of PCOS include irregular periods, excessive hair growth on the face or body, acne, weight gain, and difficulty getting pregnant.
If you think you have PCOS, see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Thyroid disease
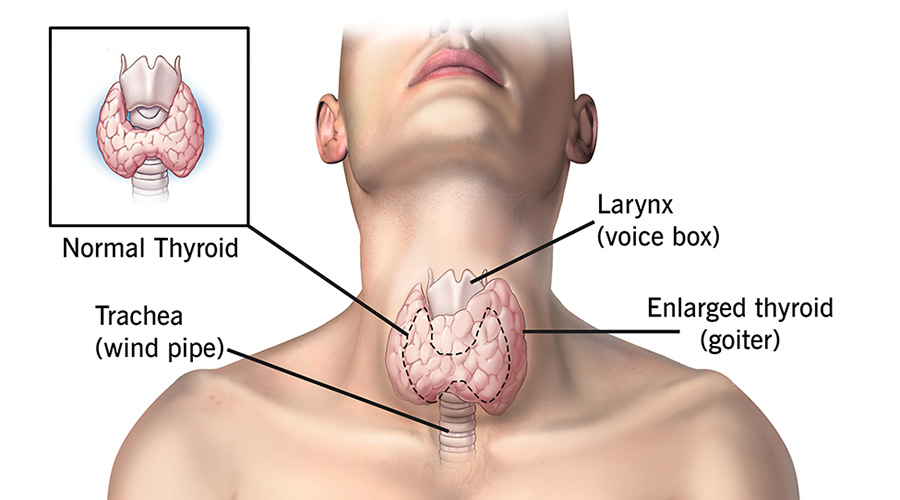
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in the neck, below Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones that help regulate the body’s metabolism. Thyroid disease can cause a number of symptoms, including weight gain or loss, fatigue, hair loss, and changes in mood. There are a number of different types of thyroid disease, including hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, and goiter. Thyroid disease is diagnosed with a blood test that measures the levels of hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Treatment for thyroid disease depends on the type and severity of the condition. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help regulate hormone levels. In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove part or all of the thyroid gland.
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding has been shown to provide health benefits for both mother and baby. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends breastfeeding as the sole source of nutrition for the first six months of a baby’s life and continuing breastfeeding until at least 12 months old. Breastfeeding also provides important immunities to newborns.

Some women find it difficult to breastfeed due to sore nipples, engorgement, or insufficient milk production. If you are experiencing difficulties breastfeeding, consult your doctor or a lactation consultant for medically reviewed treatments.
How does late ovulation affect fertility and conception?
Late ovulation can have a significant impact on fertility and conception. For women who are trying to conceive, ovulation that occurs later in the cycle can be more difficult because the chance of becoming pregnant is lower. This is because there is only a limited amount of time each month when egg cells are available for fertilization. In addition, late ovulation can also lead to irregular periods and increased chances of having a miscarriage. If you are trying to get pregnant, it is important to track your ovulation so that you can plan intercourse during your most fertile days.
How does it affect menstruation?

Late ovulation is a problem that can affect menstruation. If ovulation does not happen on time, the body may not have enough time to prepare for menstruation, which can lead to problems like missed menstrual period or light bleeding. Until you ovulate, estrogen is released, which keeps the lining of your womb growing, and then ovulation triggers the release of progesterone, which helps the lining support a fertilized egg. Even if you ovulate late, you still have a chance of “catching” your fertilized egg in your uterine lining.
Inference
In conclusion, ovulation that occurs later in the menstrual cycle is more likely to result in a successful pregnancy. This is because the chances of conceiving a baby are highest when ovulation occurs early in the cycle. For women who are trying to get pregnant, it is important to keep track of their ovulation schedule and plan intercourse accordingly. There are many ways to track and stimulate ovulation, and couples who are trying to conceive should discuss the best method for them.
Frequently asked questions
What is considered late ovulation?
Late ovulation is ovulation that occurs later than expected. For most women, ovulation occurs around day 14 of their menstrual cycles. However, for some women, ovulation may not occur until day 19 or even later. Late ovulation can be caused by a number of factors, including stress, illness, and hormonal problems. If you are trying to conceive and are not having success, you may want to consider whether you are ovulating late.
If you are trying to get pregnant and are not having success, you may want to consider whether you are ovulating late. Late ovulation can be caused by a number of factors, including stress, illness, and hormonal problems that may affect ovulation. Most women ovulate around day 14 of their menstrual cycle, but for some women, ovulation may not occur until day 19 or later.
What causes late ovulation?
Late ovulation can be caused by a number of factors, the most common being PCOS. Other causes can include thyroid disorders, premature ovarian failure, and endometriosis. If you are trying to conceive and are having difficulty because you are not ovulating at the time you expect to, it is important to see your doctor determine the cause. This will help to ensure that you receive appropriate treatment and increase your chances of becoming pregnant.
Does late ovulation affect egg quality?
The article cites a study that suggests that ovulating later in your cycle may result in lower-quality eggs. The study looked at the effect of the day of ovulation on egg quality and found that eggs retrieved on the later days of ovulation were of poorer quality than those retrieved earlier in the process. The study’s authors say that their findings could have important implications for women who are trying to conceive.
How do you know if you ovulate late?
If you’re trying to conceive, you may be wondering how to know if you ovulate late. Unfortunately, there’s no foolproof way to know for sure. However, there are some signs and symptoms that may indicate that you’re ovulating later than usual.
One sign that you may be ovulating late is if your menstrual cycle is longer than usual. Another sign is if you don’t experience any of the typical symptoms of ovulation, such as a change in cervical mucus or a rise in basal body temperature. Additionally, if you don’t get pregnant after several months of trying, it’s possible that you’re ovulating later than normal.
If you think you may be ovulating late, there are a few things you can do to increase your chances of getting pregnant. First, keep track of your menstrual cycle and note any changes in symptoms.
Is it harder to get pregnant if you ovulate late?
While there is no definitive answer to whether or not it is harder to get pregnant if you ovulate late, there are a few things to consider. First, ovulation typically occurs 14 days before the start of a woman’s period, so if you’re trying to conceive, figuring out when you ovulate is key. If you’re having trouble pinpointing when you ovulate, tracking your basal body temperature can help; your basal body temperature will spike after ovulation has occurred. Additionally, sperm can survive in the woman’s body for up to five days, so if intercourse takes place around the time of ovulation, there is a good chance of getting pregnant. Finally, if you do ovulate later than usual, it might take longer to get pregnant; however, with patience and some basic fertility knowledge, most couples should be able to conceive.

